Applying MapCalc Map Analysis Software
Mapping Wildfire Risk: A fire risk map for the project area is
needed for county-wide emergency planning.
To meet this need an initial Wildfire Risk Model was developed that
considers 1) Fuel Loading based on terrain and cover type conditions, 2)
Fire Detection based on visibility to housing and roads and 3) Fire
Response-time based on relative and absolute barriers to emergency vehicle
movement.
<click
here> for a printer friendly
version (.pdf)
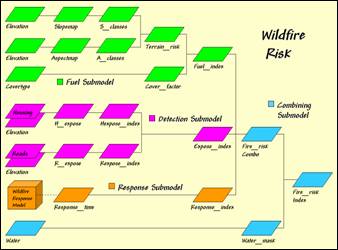
Processing Flow.
Base Maps. The Base Maps needed include:
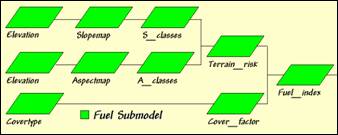 Fuel Submodel. Fuel Loading is dependent on two
factors—Terrain and Cover type conditions.
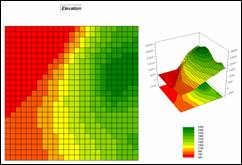
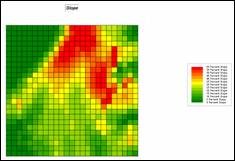
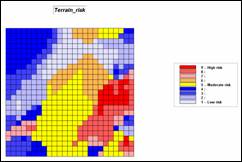
Terrain conditions assume fuel drying on steep southern slopes identify the
highest risk; gentle north-facing slopes identify the lowest; and all other
slope/aspect combinations form risk indices in between.
Fuel Submodel. Fuel Loading is dependent on two
factors—Terrain and Cover type conditions.
Terrain conditions assume fuel drying on steep southern slopes identify the
highest risk; gentle north-facing slopes identify the lowest; and all other
slope/aspect combinations form risk indices in between.
Step 1, Terrain Conditions—Slope.
SLOPE Elevation Fitted FOR
Slopemap
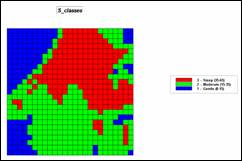
RENUMBER Slopemap ASSIGNING 1 TO 0 THRU 15 ASSIGNING 2 TO 15 THRU 35 ASSIGNING 3 TO 35 THRU 65 FOR Slope_classes
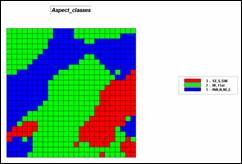
Step 2, Terrain Conditions—Aspect
ORIENT Elevation Octants FOR Aspectmap
RENUMBER Aspectmap ASSIGNING 1 TO
1 THRU 3 ASSIGNING 1 TO 8 ASSIGNING 2 TO 7 ASSIGNING 2 TO 9 ASSIGNING 3 TO 4 THRU 6 FOR Aspect_classes
Step 3, Terrain Conditions—combine Slope and
Aspect classes
INTERSECT Slope_classes WITH Aspect_classes ASSIGNING 3
TO 1
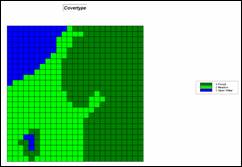
Step 4, Covertype Conditions—based on the amount
of biomass (1.0
RENUMBER Covertype ASSIGNING 0.0 TO 1 ASSIGNING 0.5 TO 2 ASSIGNING 1.0 TO 3 FOR Cover_factor
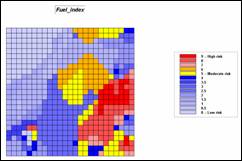
Step 5, Combine Terrain and Covertype
Conditions—update terrain risk based on cover type factor
COMPUTE Cover_factor Times Terrain_risk FOR Fuel_index
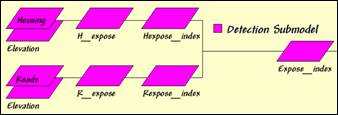 Detection Submodel. Early detection of a fire is, in large part,
dependent on visual exposure of a location to housing and roads.
Detection Submodel. Early detection of a fire is, in large part,
dependent on visual exposure of a location to housing and roads.
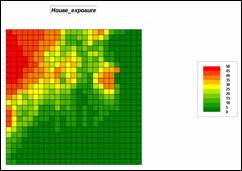
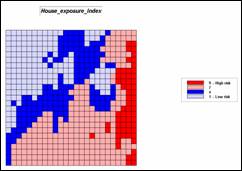
Step 6, Visual exposure to housing—determine
the number of times each location is seen from housing locations, then convert
to a visual exposure index. Note that
the areas with low visual exposure have the higher risk indices as the
probability of early detection of a fire is low.
RADIATE Housing OVER Elevation TO 35 Weighted FOR House_exposure
RENUMBER House_exposure ASSIGNING 9 TO 0 ASSIGNING 7 TO 1 THRU 8 ASSIGNING 4 TO 8 THRU 25 ASSIGNING 1 TO 25 THRU 50 FOR House_exposure_index
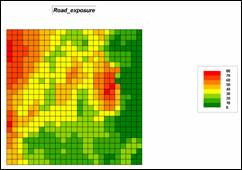
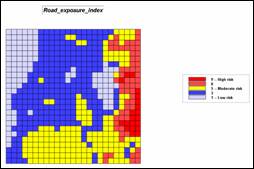
Step 7, Visual exposure to roads—determine the
number of times each location is seen from road locations, then convert to a
visual exposure index. Note that the
areas with low visual exposure have the higher risk indices as the probability
of early detection of a fire is low.
RADIATE Roads OVER Elevation TO 35 Completely FOR Road_exposure
RENUMBER Road_exposure ASSIGNING 9 TO 0 ASSIGNING 8 TO 1 THRU 10 ASSIGNING 5 TO 10 THRU 30 ASSIGNING 3 TO 25 THRU 50 ASSIGNING 1 TO 50 THRU 75 FOR Road_exposure_index
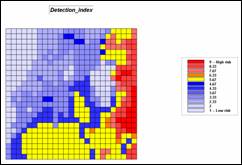
Step 8, Combined index of visual exposure to
housing and roads—the two index maps are averaged with visual exposure to roads
as twice as important in determining detection risk.
ANALYZE House_exposure_index TIMES 1 WITH Road_exposure_index TIMES 2 Mean FOR Detection_index
 Response Submodel. Response-time is dependent on both on- and
off-road travel for emergency vehicles as determined by relative and absolute
barriers derived from road type, terrain conditions and land cover.
Response Submodel. Response-time is dependent on both on- and
off-road travel for emergency vehicles as determined by relative and absolute
barriers derived from road type, terrain conditions and land cover.
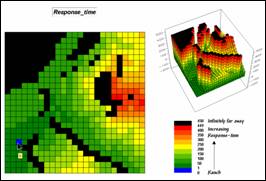
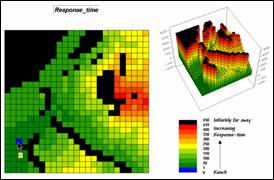
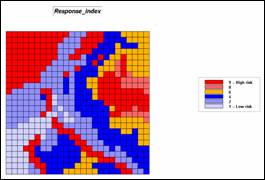
Step 9, Response-time index—the results of the
Wildfire Response Model is converted to a risk index.
RENUMBER Response_time ASSIGNING 9 TO 350 THRU 450 ASSIGNING 8 TO 275 THRU 350 ASSIGNING 6 TO 200 THRU 275 ASSIGNING 4 TO 100 THRU 200 ASSIGNING 2 TO 50 THRU 100 ASSIGNING 1 TO 0 THRU 50 FOR Response_index
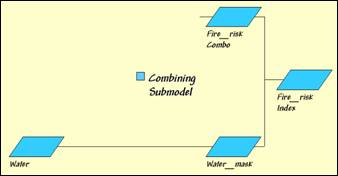 Combining Submodel. Overall Fire Risk is the combination of the
Fuel, Detection and Response indices for each map location.
Combining Submodel. Overall Fire Risk is the combination of the
Fuel, Detection and Response indices for each map location.
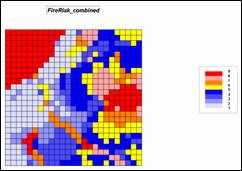
Step 10, Combined index of Fuel, Detection and
Response indices —the individual submodel results are weight-averaged with the
Detection index receiving the least weight and the Response-time index the
most.
ANALYZE Detection_index TIMES 1 WITH Fuel_index TIMES 3
WITH Response_index TIMES 5 Mean FOR FireRisk_combined
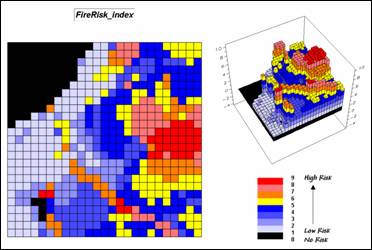
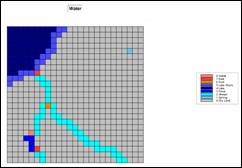
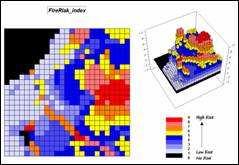
Step 11, Water mask—the overall index is
“masked” to eliminate areas of open water (can’t burn water—no fire risk).
RENUMBER Covertype ASSIGNING 0 TO 1 ASSIGNING 1 TO 2 THRU 3 FOR Water_mask
COMPUTE Water_mask Times FireRisk_combined FOR FireRisk_index
Summary. The initial Wildfire Risk Model considers Fuel Loading, Fire Detection and Fire Response in deriving an overall Fire Risk map. Areas with considerable biomass on steep southerly slopes, minimal visual exposure to houses and roads, and a long distance from where fire crews are located are assigned a high index. Several extensions, such as adjustments for seasonal and short-term weather effects, proximity to water and human activity levels would strengthen the model.